Characteristics of radio signals In high-frequency circuits, there are three main types of radio signals we want to process: baseband (message) signals, high-frequency carrier signals, and modulated signals. The so-called baseband signal is the original signal before modulation, which is also called modulated signal. 2. Spectrum characteristics? For periodic signals, it can be expressed as many discrete frequency components (the components are in a harmonic relationship), for example, Figures 1-3 are the spectrum diagrams of the signals shown in Figures 1-2; for non-periodic signals, you can use Fu The method of Fourier transform is decomposed into continuous spectrum, and the signal is the integral of continuous spectrum. Figure 1 — 3 Spectrogram 3. Propagation characteristics Propagation characteristics: refers to the propagation mode, propagation distance and propagation characteristics of radio signals. The propagation characteristics of radio signals are mainly distinguished according to the frequency band or band in which they are located. ? Figure 1-5 The main mode of radio wave propagation? 4. Modulation characteristics?
Draw-wire sensors of the wire sensor series measure with high linearity across the entire measuring range and are used for distance and position measurements of 100mm up to 20,000mm. Draw-wire sensors from LANDER are ideal for integration and subsequent assembly in serial OEM applications, e.g., in medical devices, lifts, conveyors and automotive engineering.
Linear Encoder,Digital Linear Encoder,Draw Wire Sensor,1500Mm Linear Encoder Jilin Lander Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.landerintelligent.com
1. Time characteristics
(1) Signal description: A radio signal, which can be expressed as a time function of voltage or current, is usually described by time-domain waveforms or mathematical expressions.
(2) The concept of time characteristics: The time characteristics of radio signals are the characteristics of how fast the signal changes with time. The time characteristic of the signal requires that the time characteristic of the circuit that transmits the signal (such as the time constant) be adapted to it.
For more complex signals (such as voice signals, image signals, etc.), it is more convenient to use spectrum analysis.
The concept of the spectral characteristics of a signal: The spectral characteristics of a signal are the characteristics of each frequency component in the signal. 
The spectral characteristics include amplitude frequency characteristics and phase frequency characteristics, which respectively reflect the distribution of the amplitude and phase of each frequency component in the signal.
Any signal will occupy a certain bandwidth. From the perspective of spectrum characteristics, the bandwidth is the frequency range or frequency bandwidth occupied by the main part of the signal energy (generally more than 90%). ? 
After the electromagnetic wave is radiated from the transmitting antenna, not only the energy of the radio wave will be diffused, but the receiver can only receive a very small part of it, but during the propagation process, the energy of the radio wave will be absorbed or reflected by the ground, buildings or high-altitude ionosphere , Or it may cause refraction or scattering in the atmosphere, which will greatly reduce the intensity when it reaches the receiver. According to the phenomenon of radio waves in the propagation process, the propagation methods of radio waves mainly include direct (line-of-sight) propagation, diffraction (ground wave) propagation, refraction and reflection (sky wave) propagation, and scattered propagation, as shown in Figures 1 to 5. Show. The key factor that determines the propagation mode and propagation characteristics is the frequency of the radio signal. ? 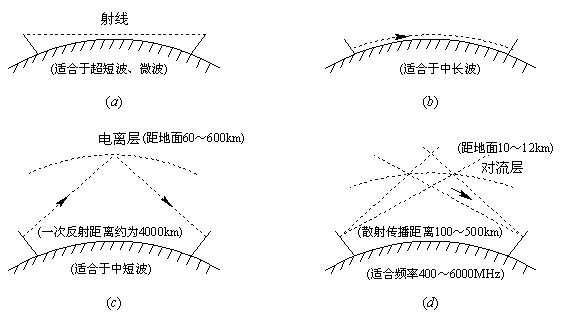
(A) Direct propagation; (b) Ground wave propagation; (c) Sky wave propagation; (d) Scattering propagation
Another reason why high frequency (radio frequency) is generally used for radio propagation is that high frequency is suitable for antenna radiation and wireless propagation. Only when the size of the antenna is comparable to the wavelength of the signal, the radiation efficiency of the antenna will be higher, so that with a smaller signal power spread over a longer distance, the receiving antenna can effectively receive the signal.
The so-called modulation is to use the modulation signal to control the parameters of the high-frequency carrier, so that one or several parameters (amplitude, frequency or phase) of the carrier signal change according to the law of the modulation signal.
According to the different modulation parameters of the carrier, modulation is divided into three basic modes, which are amplitude modulation (amplitude modulation), frequency modulation (frequency modulation), and phase modulation (phase modulation), which are respectively expressed by AM, FM, PM, and can also be combined Modulation.